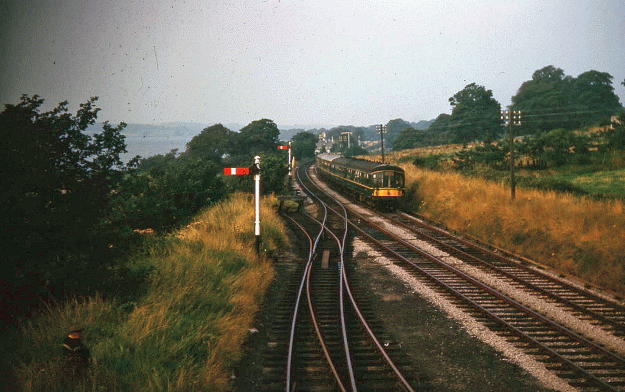
I came across a colour slide that I took as a teenager on holiday with my dad of a diesel multiple unit approaching Caernarfon (then spelled ‘Caernarvon’ by the railway authorities) in the summer of 1963. DMUs were still a novelty in those days.
We didn’t travel there by rail: my dad was by then the proud owner of a Morris Minor convertible which he called Gladys.
In the 1980s I walked down the trackbed through the cutting that led from the site of Caernarfon station beneath the town centre and into a short tunnel leading to the Slate Quay.
Later still, when the tunnel became an underpass, I drove my car through it.
Remembering this prompted me to look up Caernarfon railway station on the compendious Subterranea Britannica website: Disused Stations: Caernarvon Station (disused-stations.org.uk).
There I found an entertaining anecdote about Caernarvon No 1 signal box which controlled movements east of the station towards Menai Bridge.
Apparently, this box had for decades proved difficult to man because crews were intimidated by a colony of rats who liked to dine on the grease that lubricated the machinery beneath the floor.
The rats didn’t seem to mind the humans at all, but the railwaymen tired of hordes of rodents climbing all over the place.
When services south of Caernarfon ceased in 1964 the station became a terminus. The track layout and signalling was altered and the No 1 signal box was closed and its mechanism dismantled.
There followed an unrepeatable public entertainment.
The wooden structure was soaked in paraffin and surrounded by dogs. When the building was set on fire, hundreds of rats raced for safety and the dogs captured only a few.
The survivors spread across town and were for some time an inconvenience.
Nowadays, it seems, rats are no more a problem in Caernarfon than anywhere else: Are you never more than 6ft away from a rat? – BBC News.
It’s once more possible to catch a train from Caernarfon, southwards over the 2ft-gauge Welsh Highland Railway, opened in 1997: Home Page – Ffestiniog & Welsh Highland Railways (festrail.co.uk).



